Hey coders! This is a blog figured out for beginners in competitive programming. It's been a month since I started competitive programming in the Hackerrank platform. I just tried to pass the test cases of the "Problem solving(Basic)" skill certification. I was given two tricky problems with 1.30 hours of time to complete it. The two problems covered basic topics of Data Structures (such as Arrays, Strings) and Algorithms (such as Sorting and Searching). The problem titles were: 1) Unexpected Demand 2) Road Repair
This is the solution to this problem and it passes all the test cases!
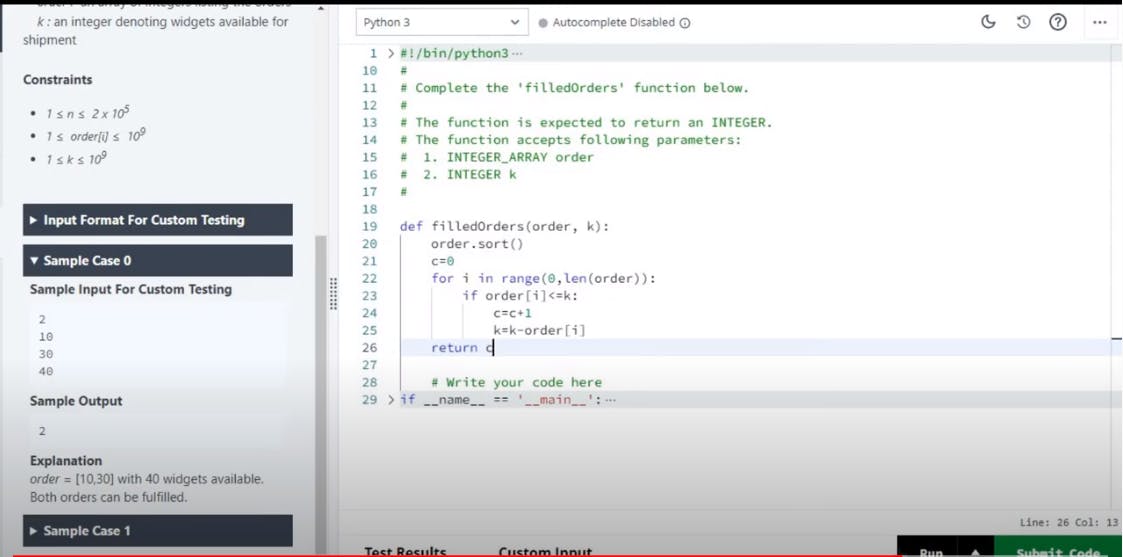
Let's have look at the detailed problem statement
This is the main parameter to write down your code : The sample input and the sample output.
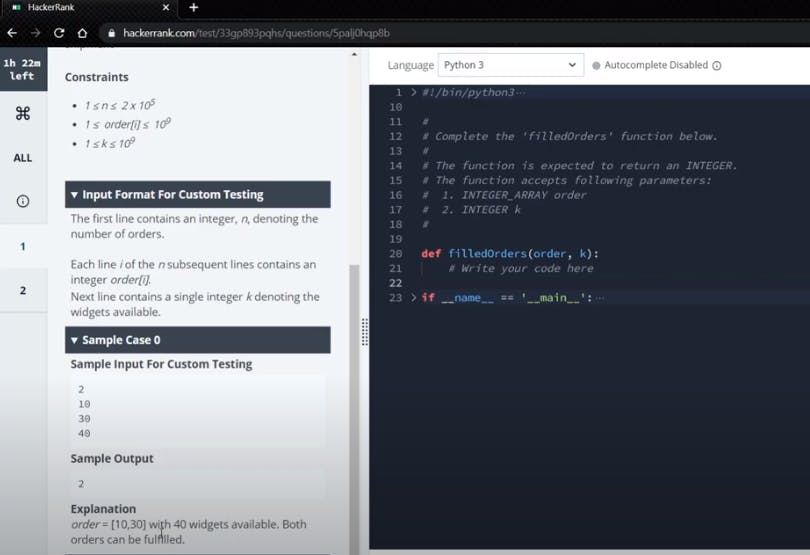
The basic idea is to initialize count (c) and sort the list first and then if order[i] is less than or equal to k increment c by 1 and assign k as k-order[i]. Else, return c which provides the count. This was moderately simple! Next, we move on to another tricky problem which took me almost 45 minutes to crack it! The implementation is on JAVA. Frankly, I wanted to do in JAVA even though it will turn out easier with python because, I thought that it will help me to understand my semester's portions in my UG (B.E).
Road Repair A number of points along the highway are in need of repair. An equal number of crews are available, stationed at various points along the highway. They must move along the highway to reach an assigned point. Given that one crew must be assigned to each job, what is the minimum total amount of distance traveled by all crews before they can begin work?
For example, given crews at points {1,3,5} and required repairs at {3,5,7}, one possible minimum assignment would be {1→ 3, 3 → 5, 5 → 7} for a total of 6 units traveled.
Function Description
Complete the function getMinCost in the editor below. The function should return the minimum possible total distance traveled as an integer.
**getMinCost has the following parameter(s):
crewId[crewId[0],...crewId[n-1]] : a vector of integers
jobId[jobId[0],...jobId[n-1]] : a vector of integers**
Constraints
1 < n < 105
crewId[i] : 1 < crewId[i] < 109
jobId[i] : 1 < jobId[i] < 109
Input Format For Custom Testing
The first line contains an integer, n, denoting the number of elements in crew_id and job_id.
Each line i of the n subsequent lines (where 0 < i < n) contains an integer describing crew_id[i].
The next line again contains the integer n as above.
Each line i of the n subsequent lines (where 0 < i < n) contains an integer describing job_id[i].
Sample Case 0 Sample Input For Custom Testing
5
5
3
1
4
6
5
9
8
3
15
1
Sample Output
17
Explanation
By index, crewId[i] → jobId[i], { (0 → 0) , (1 → 2) , (2 → 4) , (3 → 3) , (4 → 1) } is one possible assignment for a minimum cost of 17. Showing element values, this is { (5 → 9) , (3 → 3) , (1 → 1) , (4 → 15) , (6 → 8) } yielding a total travel distance of 4 + 0 + 0 + 11 + 2 = 17.
Sample Case 1
Sample Input For Custom Testing
4
5
1
4
2
4
4
7
9
10
Sample Output
18
Explanation
By index, { (1 → 0) , (0 → 1) , (2 → 2) , (3 → 3) } is one possible assignment for a minimum cost of 18.
Java Code:
public static long getMinCost(List<Integer> crew_id, List<Integer> job_id) {
long cost=0;
Collections.sort(crew_id);
Collections.sort(job_id);
int len1=crew_id.size();
int len2=job_id.size();
if(len1==len2)
{
for(int i=0;i<len1;i++)
{
if(job_id.get(i)>=crew_id.get(i))
{
cost=cost+(job_id.get(i)-crew_id.get(i));
}
else if(job_id.get(i)<crew_id.get(i))
{
cost=cost+(crew_id.get(i)-job_id.get(i));
}
}
}
return cost;
}
